ICH Q3D Analysis (Elemental Impurities) - Interview
Behind the analysis, the faces of FILAB expertise
ICH Q3D analysis, what's the situation?
Hello, my name is Clément Boenard, and I am Head of the Inorganic Chemistry Department at FILAB. Today, I am going to talk to you about ICH Q3D analysis, an analysis that my teams and I regularly perform in our laboratory.
Hello Clément, can you explain what ICH Q3D is? And what does it involve?

Hello, ICH Q3D is a guideline that outlines a process for evaluating and controlling elemental impurities in drugs produced using risk management principles.
Its purpose is to develop a control strategy to limit specific elements such as impurities in pharmaceutical products.
Elemental impurities—what exactly are we talking about?
So, to explain what elemental impurities are, we talk about them in pharmaceutical products, they can come from several sources:
- Residual catalysts that have been intentionally added during manufacturing.
- Impurities in the strict sense of the word, such as impurities that can appear through interactions with production, processing, or even packaging equipment.
- Or components of the medicinal product.
It is also important to understand that… elemental impurities do not provide any therapeutic benefit to the patient, which is why their levels in the medicine must be controlled within acceptable limits.
To date, 24 impurities have been identified in four classes:
Translated with DeepL.com (free version)

Why is it important to perform these elemental impurity analysis? What are the risks for manufacturers, patients, etc.?
If elemental impurities are present in a drug, there is a risk that a patient treated with that drug will ultimately be administered elements that are known to be toxic. This can lead to immediate or long-term adverse effects.
For pharmaceutical manufacturers, failure to comply with these limits can result in the withdrawal of non-compliant products from the market. However, companies may also be subject to fines or other penalties, or have their marketing authorization for their drug suspended. If elemental impurities are present in a drug, there is a risk that a patient treated with this drug will ultimately be administered substances that are known to be toxic. This can lead to immediate or long-term adverse effects.
As for pharmaceutical manufacturers, failure to comply with these limits may result in the withdrawal of non-compliant products from the market. Companies may also be subject to fines or other penalties, or have their marketing authorization for their drug suspended.
Can you explain how it works? What technique is used?

To date, at the FILAB laboratory, our teams use ICP-MS to detect and quantify elemental impurities. The analytical process involves dissolving the drug or finished product using acids. Once we have solubilized the product in an acidic environment, the resulting solution is injected into the ICP-MS. At this stage of the analysis, the response obtained is compared to a calibration range, which allows us to determine the concentration of impurities in the product.
And after all these analysis carried out in your Inorganic Chemistry Department, can you tell us if there is a potential source of elemental impurities in pharmaceutical products?
To date, I think it is important to emphasize that in more than 98% of the cases we have handled, there were no elemental impurities quantified above acceptable thresholds. And for the remaining 2%, we were able to identify that the impurities found came either from catalyst residues or from interactions with the production environment, such as a feed pipe.
Are there threshold criteria established by ICH Q3D? If so, do these thresholds influence the formulation and manufacture of pharmaceutical products?
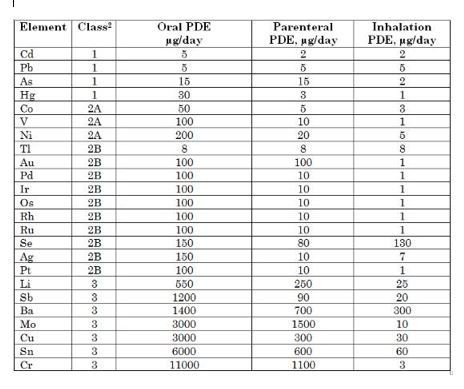
Oui il y a bien en effet des seuils qui sont définis par l’ICH Q3D. La guideline ICH Q3D définit des PDE ce qui signifie « Permitted Daily Exposure ». C’est une limite d’exposition pour chaque impureté. Pour le calcul des PDE plusieurs critères sont pris en compte dont les modes d’administration et la posologie du médicament. Ainsi nous pouvons avoir pour chaque impureté des seuils différents.
How does the analysis of elemental impurities according to ICH Q3D help to ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical products for patients worldwide?
It is important to note that the analysis of elemental impurities according to ICH Q3D guarantees the safety of drugs by ensuring the absence, up to a certain threshold, of elements that could be considered toxic to the body.
Can you tell us about the ICP training courses we offer at FILAB?
We recently conducted two ICP training sessions for our clients. In the first case, our client wanted to gain a better understanding of how we perform analysis and process samples in the laboratory. We therefore organized a two-part training session, with a theoretical section on ICP MS and ICH Q3D, followed by a practical section with live analysis monitoring.
In the second case, we conducted a training course on method development and validation for the validation of 24 impurities and the transfer of the method in-house at our client’s premises.
Thank you, Clément, for these explanations and your feedback.


