Industrial marking on metal parts: cleaning process
The problem?
What is the approach for conducting a cleaning process study in the context of industrial marking?
Industrial marking is an essential practice in many sectors, including aerospace, medical devices, automotive, and more. It is a method used to inscribe information on products or components, such as serial numbers, barcodes, manufacturing dates, logos, or any other specific instructions. These markings are crucial for traceability, quality management, regulatory compliance, and product safety.
Background to the cleaning process study
First, FILAB's client performs surface treatment on nickel joints. This involves laser texturing, a surface treatment that creates effects or gives new properties to all types of materials depending on the desired function.
This laser marking leaves behind a small amount of dust.
The study will focus on measuring the amount of nickel dust deposited on the parts after marking and comparing three post-marking cleaning processes.
Three samples are analyzed for the comparative study:
- untreated (without cleaning),
- cleaning with solvent and ultrasound,
- cleaning with a brush and blowing.
Measurement of nickel content and comparative study
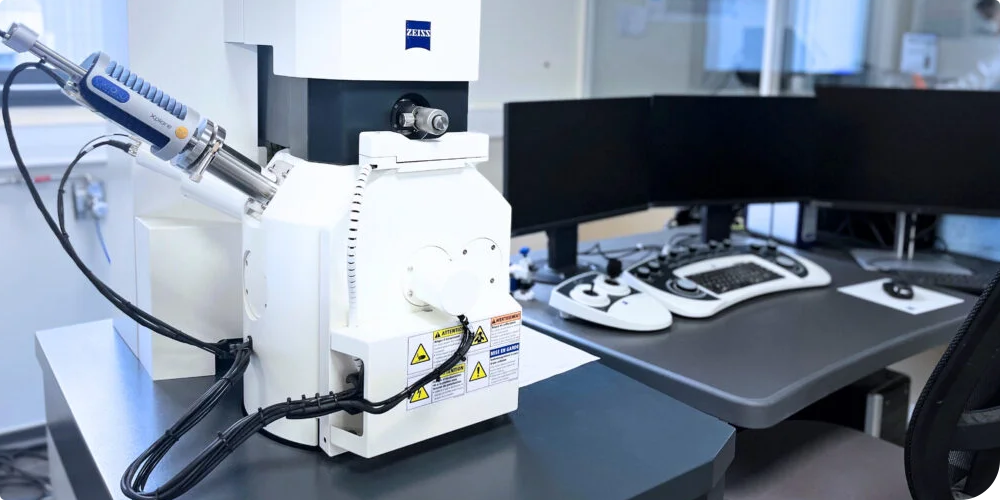
SEM-EDX Analysis (Scanning Electron Microscope)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM-EDX) technology is a well-known and recognized technique. It produces very high-resolution images of a sample's surface (magnification of around *1,000,000). It is used to study the chemical composition and morphology of solid materials.
In this specific context, SEM-EDX analysis of nickel (Ni) joints reveals:
- The presence of particles around each hole on all textured parts.
- The surfaces of the holes, on the other hand, do not show any particles, only cavities resulting from laser marking.
- The quantity of particles appears to be lower on cleaned parts (brushing + blowing) than on raw parts.
- However, it is difficult to determine whether the quantity of particles is lower on parts degreased by ultrasound.
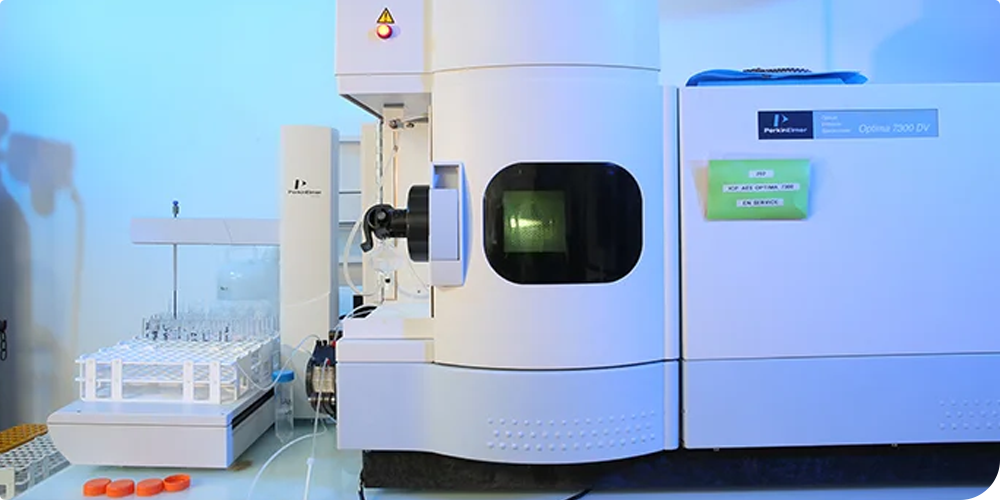
Additional analysis by ICP-AES
ICP-AES is a cutting-edge technique that uses inductively coupled plasma to excite atoms and ions in a sample, producing light emissions specific to each element. Thanks to its sensitivity and ability to analyze multiple elements simultaneously, ICP-AES is an essential tool for accurate and rapid characterization of materials.
ICP-AES analysis highlights that:
- The nickel content obtained is lower for brushed and degreased products than for those analyzed without cleaning.
- The treatments therefore do have the effect of reducing the nickel content and thus the quantity of particles present on the parts.
- Cleaning by brushing and blowing appears to be slightly more effective than degreasing with ultrasound.
Additional analysis using FTIR
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) is an analytical technique used to obtain the absorption spectrum of a solid, liquid, or gaseous sample. FTIR chemical analysis are non-destructive and measure the amount of light absorbed by a sample. This is done based on the wavelengths emitted by an infrared beam.
In this study, FTIR was used to detect the presence of polylactate and cellulose particles (related to the brushing of the parts).
Conclusion of the study
The analysis carried out by FILAB shed light on the interaction between unwanted particles and the surfaces of treated parts, highlighting the crucial importance of carefully selecting the appropriate cleaning processes.
For FILAB's client, it is essential to adopt a methodical approach when choosing these methods, taking into account not only their effectiveness in removing contaminants but also their ability to preserve the structural and functional integrity of the parts.
Thus, after analysis and expert assessments have been carried out, the client is in a position to make the best decision according to their needs.



