Extractables and leachables testing (E&L)
FILAB provides E&L testing services, including extractables testing and leachables studies, to help ensure the safety and compliance of pharmaceutical packaging and medical devices. Our advanced analytical techniques deliver reliable results aligned with regulatory standards.
Would you like to carry out a study of the Extractables and Leachables of your products?
What are Extractables and Leachables ?
Analysis of Extractables and Leachables (E&L)
The study of extractables and leachables is an essential analysis for guaranteeing the safety of materials coming into contact with sensitive products (drugs, medical devices, cosmetics, etc.).
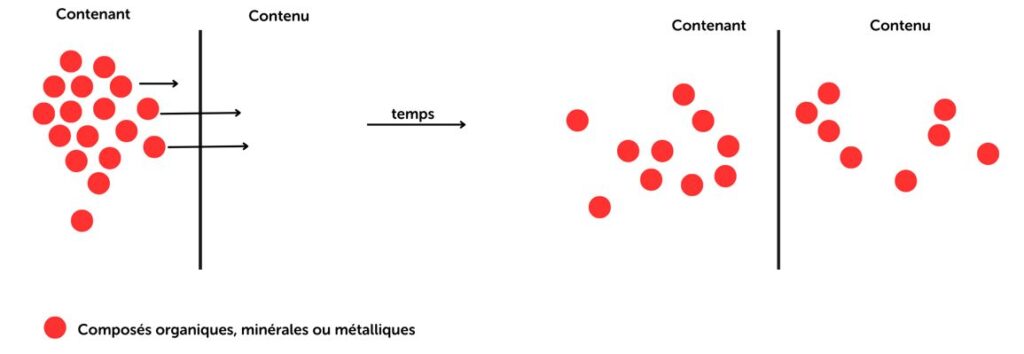
Extractables are substances that can be extracted from a material when it is subjected to aggressive solvents under controlled conditions (temperature, pH, time).
Leachables are compounds that actually migrate from a material to a finished product under normal conditions of use.
Materials concerned
Studies of extractables or leachables can be done on different types of materials or compounds : polymer additives, plasticizers, stabilizers, colorings, metallic catalysts and other chemical substances posing a contamination risk to a product.
Any substance susceptible of comping into contact with a product during the production process or at any point all the way till the implementation of the finished product must be subject to rigorous analysis and inspections to confirm that said substance has not contaminated the product.
Why carry out an analysis of extractables and leachables ?
Extractables and leachables analyses are used to assess the risks of substances migrating from a container (packaging) to the contents (product). They are used in particular in the pharmaceutical, cosmetics and medical devices sectors.
Thanks to its expertise and state-of-the-art equipment, the FILAB laboratory can support you at every stage of the assessment of extractables and leachables. Contact us for a personalised study tailored to your sector of activity.
Our solution :container/content compatibility tests and analysis of potential migration of extractables and releargables
With a varied analytical fleet and dual expertise in chemistry and materials science, the FILAB laboratory can assist you at each step of the evaluation process of extractables and of leachables in health products (medical devices, pharmaceutical products, cosmetic products) by providing the following services :
Our services
Quantitative analysis of leachable substances (organic and inorganic analysis : volatile, semi-volatile and non-volatile substances)
Stability and compatibility analysis of extractables and leachables
Literature reviews and drafting of a custom study schedule for analyzing extractable and leachable substances
Our services for medical devices
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of extractables in Medical devices
Chemical characterization of materials in Medical devices in accordance with ISO 10993-18 : polymers, ceramics, metallic parts
Material characterization in accordance with ISO 10993-12 and 10993-18
Degradation product and leachable substance analysis of medical devices
Material extractables profiles
Understanding material extractables profiles is a key step in identifying potential risks in pharmaceutical or medical packaging systems. FILAB uses advanced analytical techniques to characterize compounds that may migrate under specific conditions, helping manufacturers select safe and compliant materials early in the development process.
Pharmaceutical packaging compatibility
Evaluating pharmaceutical packaging compatibility is critical to preventing contamination and maintaining drug stability. Through extractables and leachables testing, FILAB assesses the interaction between your packaging materials and drug products to ensure safety, efficacy, and compliance throughout the product lifecycle.
Our analytical methods for extractables and leachables
GC-MS, HPLC or UHPLC/MS/MS for the detection, identification and quantification of organic compounds present in solvents, anti-UV material additives, antioxidants, dyes, inks, detergent residues, sterilisation residues, polymer residues, etc., which have been extracted and/or released from the material by a standardised simulant.
UV-visible spectrophotometry for the determination of Chromium VI released by materials such as metal alloys
ICP-AES and ICP-MS, particularly suitable for mineral or metallic pollution or additives, such as heavy metals, mineral or metallic fillers, dyes, etc.
SEM-EDX microscopy, a truly rapid and versatile diagnostic tool for diagnosing the surface condition of materials after ageing, and for observing particles, deposits, etc.
The FILAB laboratory assists manufacturers in the study of extractables and leachables
The study of E&L applies to several sectors where the interaction between materials and finished products is critical:
- Pharmaceuticals: Contact between containers (bottles, syringes, blisters) and medicines.
- Medical devices: infusions, catheters, implants, tubing.
- Biotechnology: Cell culture media, single-use systems.
- Cosmetics: Packaging and applicators in contact with sensitive formulas.
- Agri-food: Packaging and potential migration of chemical substances.
In general, the material manufacturer knows the type of compounds that can be extracted and ideally provides the user with a list of extractable chemical species. By analogy, extractables are therefore compounds that migrate from a material in the presence of a formulation under normal conditions of use. Information on extractables can be useful when testing for specific salts.
As a specific formulation can have an effect on the type and amount of salts, it is the manufacturer's responsibility to demonstrate that the level of salts does not contribute to adverse toxicological effects. Current guidelines (e.g. "Container Closure Systems for Packaging Human Drugs and Biologics" from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)) and the "Guideline on Plastic Immediate Packaging Materials" from the European Medicines Agency (EMA) clearly state that it is preferable to test for leachables with the final formulation.
In this context, FILAB has managed to implement extraction and leaching techniques described in standards and guidelines (USP 1663 and USP 1664, EN 1186, EN 1388-2, ISO 10993-12…) and in accordance with relevant national or European standards. Moreover, FILAB develops protocols specific to clients’ challenges with the aim of simulating real conditions of contact between a container and its contents to be able to analytically determine their chemical compatibility and to evaluate their level of chemical inertia. Testing chemical inertia consists of demonstrating a containers ability to resist the invasive effects of its contents which are susceptible of extracting and/or leaching chemical compounds.
With extensive experience in implementing these techniques and in developing specific analytical techniques, FILAB can assist you in the context of a study into E&Ls and studies of ageing materials.
Why choose FILAB for E&L Studies?
With over 30 years of experience in analytical chemistry, FILAB is a trusted partner for Extractables and Leachables (E&L) studies. Our ISO 17025-accredited laboratory offers a comprehensive suite of state-of-the-art analytical techniques, including GC-MS, LC-MS, ICP-MS and FTIR, to detect and quantify extractables and leachables in compliance with USP <1663>, <1664>, ICH Q3D and EMA/FDA guidelines.
Our experts support you at every stage of your project—from method development and material compatibility assessments to full regulatory submission support. Whether you’re qualifying pharmaceutical packaging, drug delivery systems, or medical devices, FILAB delivers reliable, customized and regulatory-compliant E&L testing solutions tailored to your needs.
FAQ
Correlation of extractables data with potential leachables must be done with caution, as not all leachables are found in extractables studies. Since a drug formulation can chemically alter known extractables, it is possible to detect leachables that were not detected by the extractables study.
In addition, sample matrix effects, differences in the analytical system, changes in the test method, etc., limit the possibility of direct correlations.
The evaluation of a material, its ageing over time and the compatibility of materials and objects (polymer, metal or glass containers) in contact with its contents (cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, food, medical devices, etc.) is a major concern for manufacturers in the food, cosmetics, pharmaceutical and medical device industries. The impact of chemical migration from the material (container, packaging, crockery, utensil, implant, equipment, etc.) in contact with the product (medical devices, bulk, powder, tablet, liquid, human body, etc.) can be critical: pollution, non-compliance, complaints, harm to consumers/users, etc.
In 1999, for example, the FDA published Guidance for Industry: Container Closure Systems for Packaging Human Drugs and Biologics, which specifies that :
‘Packaging components must be made of materials that do not release undesirable or hazardous substances to the patient treated with the product.
Consequently, the dossiers must contain extraction tests on the packaging to determine which chemical components or materials are likely to migrate into the product. A study of the toxicity of these components must be carried out’.
In 2005, this text was supplemented by a European guideline issued by the EMA: Guideline on plastic immediate packaging material, which specifies that the aim of extraction tests is to identify and quantify additives (antioxidants, plasticisers, catalysts, etc.) that may be extracted by the contents in contact with the packaging, whether the product is liquid or solid.
Following this, in 2006, the Product Quality Research Institute (PQRI) carried out in-depth research into products that are inhaled or administered by the nasal route.
These studies led to recommendations: Safety Thresholds and Best Practices for Extractables and Leachables in Orally Inhaled and Nasal Drug Product.
These recommendations now serve as a reference for the FDA and the rest of the pharmaceutical world.
These studies mainly concern packaging components (blisters, bottles, pre-filled syringes, metering valves, inhalers, etc.), but also those in contact with the product during the manufacturing process (filtration systems, transfer tubes, disposable equipment, big bags, etc.).
The substances released may have an effect either on the patient, such as proven carcinogenicity (N-nitrosamines, polyaromatic hydrocarbons, etc.), or on the physico-chemical stability of the drug itself.
The main challenges are regulatory compliance, material variability and interpretation of results. The pharmaceutical and medical industries must comply with strict standards (USP, ISO 10993, ICH Q3D), which requires in-depth analysis and rigorous validation. The complexity of modern materials (multilayers, coatings, technical polymers) can lead to unpredictable migration behaviour. Finally, interpreting the data requires specialised expertise to distinguish critical impurities from risk-free compounds, while guaranteeing the safety of the end product.
Extractables are substances that can be extracted from a material when it is subjected to specific solvents under controlled conditions. Releasables, on the other hand, are substances that actually migrate from the material into the finished product under normal conditions of use.
The study of leachables is more representative of the real risk to the end user.
Medical devices are in direct contact with biological fluids, medicines or injectable solutions. An E&L study can identify substances that may migrate and verify their safety. This analysis is essential to meet biocompatibility requirements, as defined in ISO 10993-18.
The materials concerned are those in direct contact with a sensitive product: plastics, polymers, rubbers, metals, inks and adhesives. These materials are found in pharmaceutical packaging, syringes, tubing, infusion bags and medical implants.
The FDA does not have a specific guideline dedicated to E&L, but it does address these aspects in several regulatory documents, notably for medical devices (ISO 10993-18), pharmaceutical packaging and drug delivery systems. The agency recommends in-depth studies to identify potential impurities that may migrate into medicines, and assesses their toxicological impact in terms of acceptable safety thresholds. The FDA's expectations are in line with those of the US pharmacopoeias (USP <1663>, <1664>) and international recommendations such as those of the ICH.
USP defines the requirements for extractables and leachables (E&L) in materials in contact with pharmaceutical products through USP <1663> and USP <1664>.
USP <1663> describes the principles and methodologies for identifying extractables, i.e. substances that can be extracted from a material under aggressive conditions. USP <1664> concerns leachables, which are compounds that actually migrate into the finished product under normal conditions of use.
These guidelines help to ensure patient safety and regulatory compliance by characterising potential impurities that may affect the stability and safety of medicines.
Extractables are compounds that can be released from a material under aggressive conditions, while leachables are those that migrate under normal usage conditions
To assess potential chemical interactions between packaging and drug products, ensuring patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Plastics, elastomers, glass, single-use systems, containers, closures, tubing, syringes, and medical device components.








